
Last year, researchers at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew gardens, found 74 new plants and 15 fungus, ranging from a subterranean “forest” to magnificent orchids.
Numerous enigmatic organisms were discovered in improbable locations, including clinging to Antarctic rocks or the summit of volcanoes.
The experts claim that at least one of the new discoveries has likely already been lost and that they require immediate protection.
The extinction of over 75% of undescribed plants is a threat.
The top ten species that scientists have identified as being new to science in 2023 serve as both a sobering warning about the perils of climate change and biodiversity loss, as well as a reminder of the wonder and beauty of the natural world.

The first stage in establishing safeguards and looking into possible applications for humans, according to senior research leader Dr. Martin Cheek, is giving a species a scientific name.
“The sheer sense of wonder when you realise that you’ve found a species that is totally unknown to the rest of the world’s scientists and in fact everyone else on the planet, in many cases, is what makes life worth living,” he stated to BBC News.
“It’s a huge boost.”
The top ten discoveries made worldwide by Kew in 2023 are:
Three novel Antarctic fungal species
There are very few flowering plants in Antarctica, however lichens can grow on sparse patches of exposed bare rock.
Slightly more than 5–10% of all known fungal species are found worldwide, not just in isolated, uncharted regions.
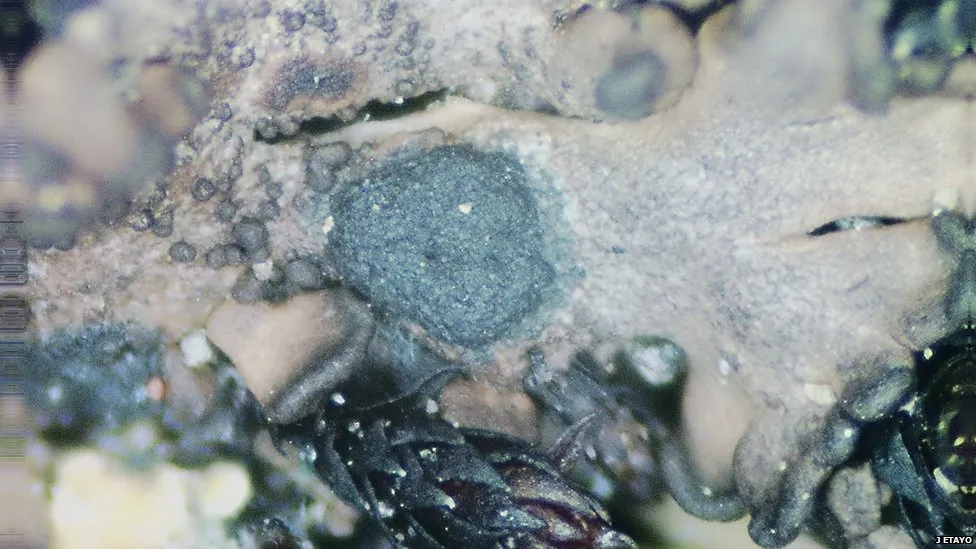

With such diversity, “we are bound to discover new sources of food, medicines and other useful active compounds that can help us find nature-based solutions to some of the biggest challenges we face today,” according to Dr. Raquel Pino-Bodas, the fungal expert at Kew.
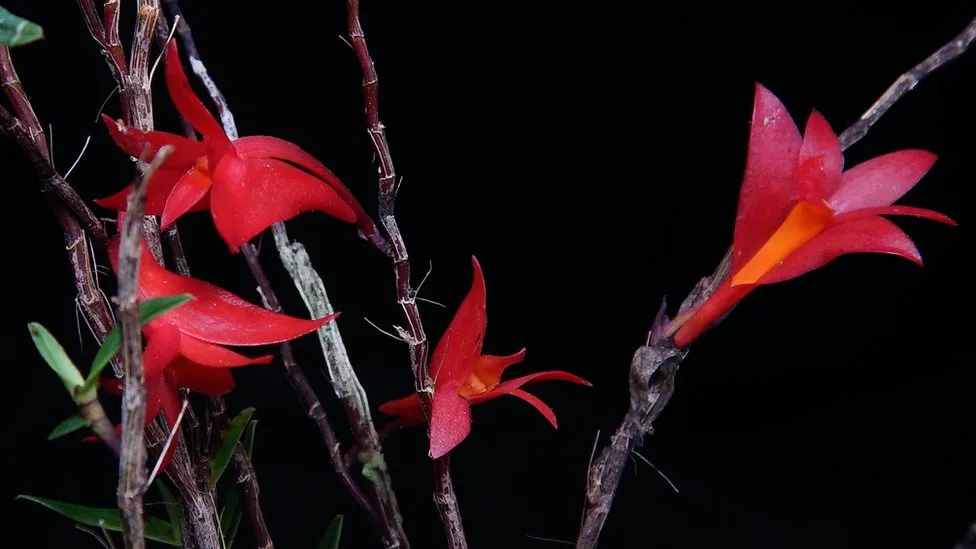
An orchid discovered atop a volcano
On the Indonesian island of Waigeo, the plant with its amazing vivid red blossoms was discovered growing on the peak of Mount Nok, an extinct volcano.

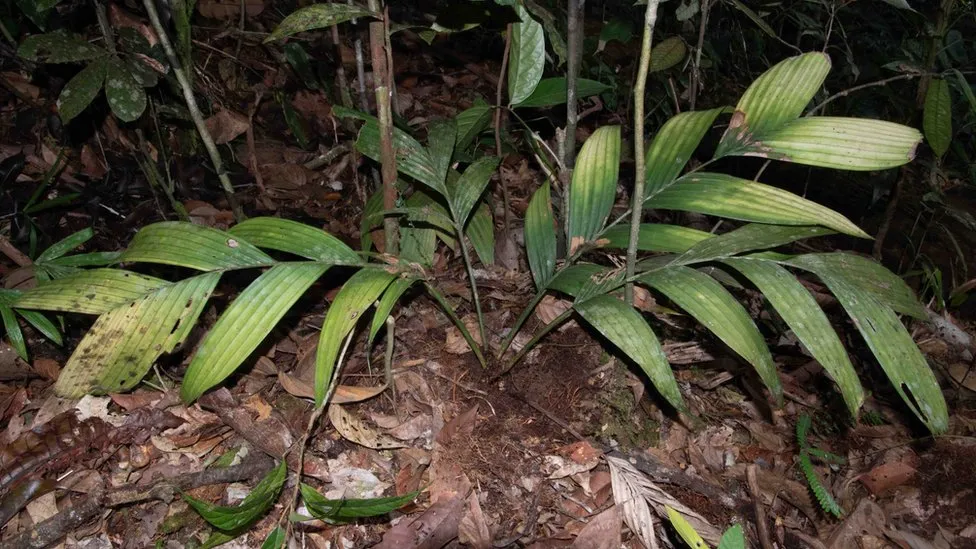
a subterranean palm
The palm, Pinanga subterranea, was discovered in Borneo, a South East Asian island.
Most of the vivid red fruits and blossoms are buried beneath the ground.

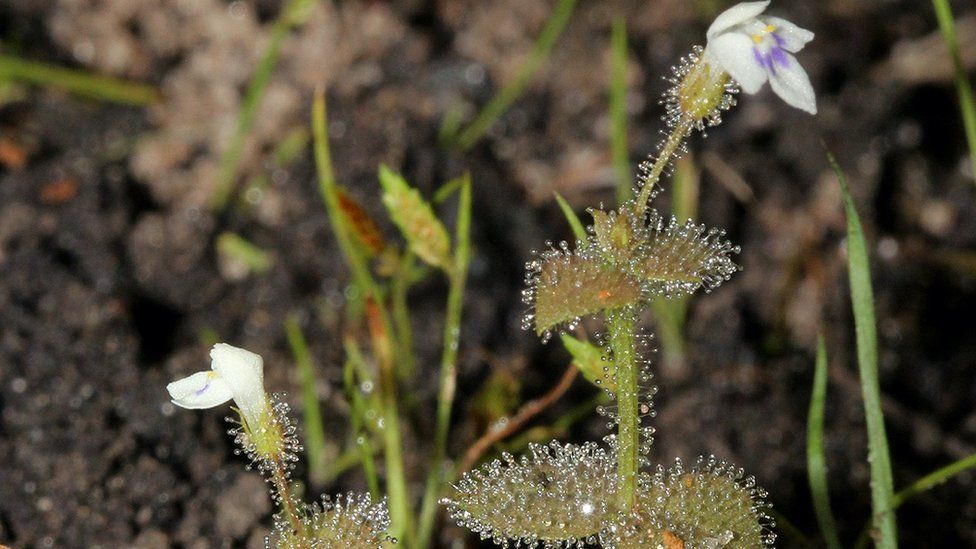
A potential plant from Mozambique that consumes meat
The unusual plant, Crepidorhopalon droseroides, belongs to the mint family and is unrelated to other carnivorous plants. It uses sticky hairs to capture and trap insects, which it may then digest for sustenance.
“I put my money on it being proved as carnivorous scientifically in the next few years,” stated Dr. Cheek.
“And if that is verified, this will be a new occurrence of the evolution of carnivorous plants being recorded.”
Two trees that spend almost all of their time underground
The trees were found growing in central Africa’s highland Angola, beneath the Kalahari sands.
The surface only shows minor details, like the flowers.
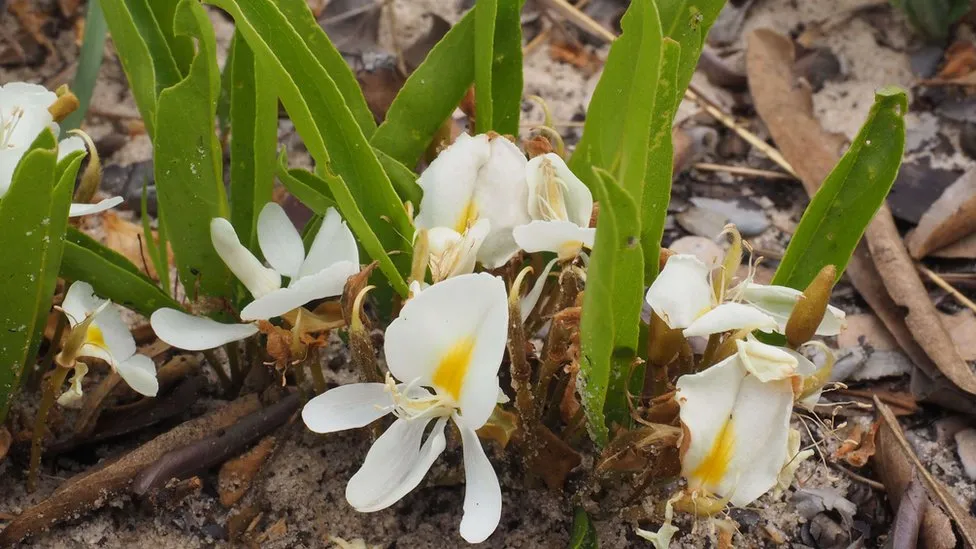

One is a member of the bean family and has white blossoms; it’s called Baphia arenicola, meaning “growing on sand”. The second plant bears vivid yellow flowers, Cochlospermum adjanyae.
“This is such a curiosity for scientists and here are two new species of these very little but very curious underground forests,” said Dr. Cheek.
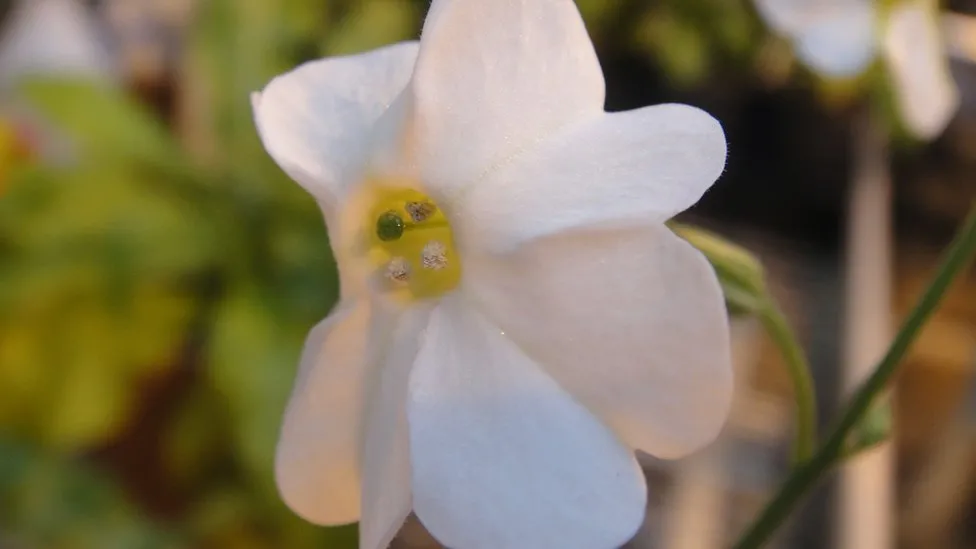
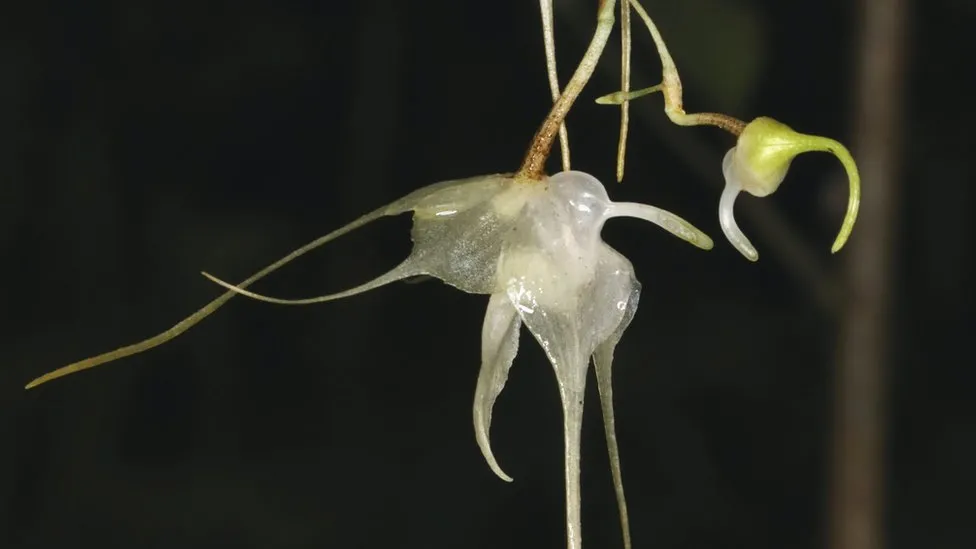
An orchid that is new was found on the island of Madagascar.
The oddly lovely bird with a blue beak that draws tourists—the helmet vanga—is responsible for the plant’s survival.
Because villagers have preserved the areas of woodland where the bird resides, the orchids’ pale, translucent blossoms have been protected.

Additional findings consist of:
- Fungi discovered in South Korea growing on food waste;
- a Thai flower like a violet;
- a South African shrub that yields indigo
Every year, scientists discover roughly 2,500 new plant species and 2,500 new fungal species on average; nevertheless, it’s thought that up to 100,000 plant species are still unidentified.
The number is significantly higher for fungus.




More Stories
Trial for Rape and Human Trafficking will take Place in Romania for Andrew Tate and his Brother Tristan
A British individual tests the first Customised Melanoma Vaccination
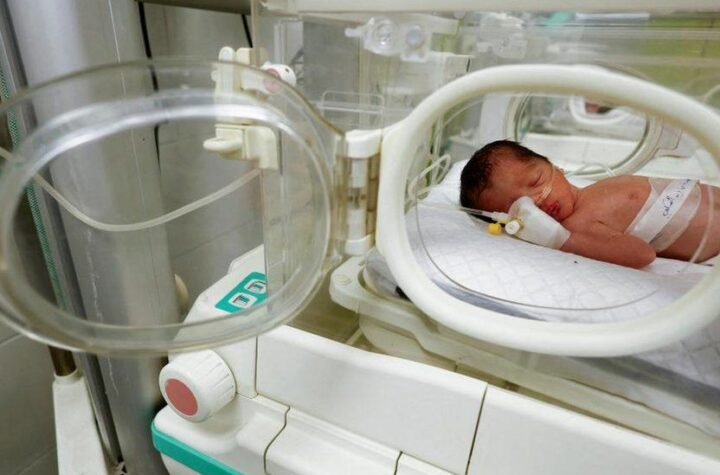
Gaza Baby Delivered from Dead Mother’s Womb Perishes